As we embark on 2024, the manufacturing industry stands at the forefront of a green revolution. Driven by technological advancements, regulatory changes, and a growing consciousness about sustainability, manufacturers are rapidly adopting new trends.
This article covers twenty green manufacturing trends for 2024, each representing a stride towards a more sustainable, efficient, and innovative industrial future.

1. Closing the Sustainability Gap
The manufacturing sector is actively working towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions, embracing ESG goals, and aiming for Net Zero emissions to bridge the sustainability gap. Manufacturers are implementing comprehensive sustainability strategies, including energy-efficient practices, waste reduction initiatives, and responsible sourcing of materials.
This holistic approach not only benefits the environment but also enhances brand reputation and competitiveness in a market where sustainability is increasingly a differentiating factor.
2. Generative AI in Automation
Generative AI is revolutionizing manufacturing by enhancing automation, enabling hyper-personalization, and predicting market demands. By leveraging generative AI algorithms, manufacturers can optimize production processes, customize products on a mass scale, and minimize material waste.
This technology also empowers companies to adapt swiftly to changing consumer preferences, reducing overproduction and conserving resources in the process.
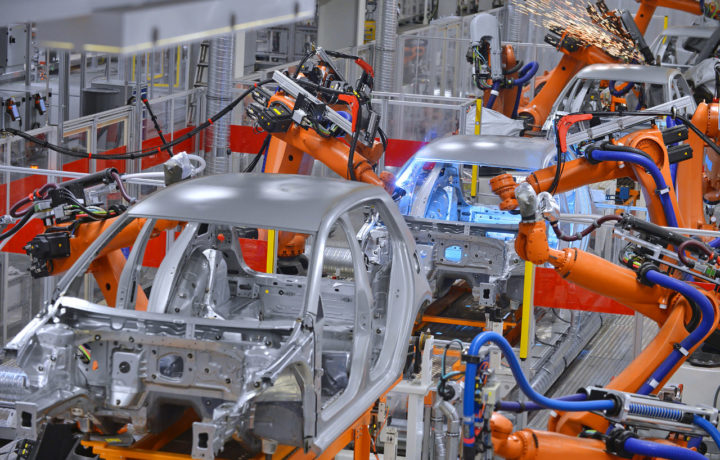
3. Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are making manufacturing processes more efficient and sustainable, reducing energy consumption, emissions, and waste.
The integration of advanced robotics and automation systems allows for precise control of production, leading to higher product quality and consistency. Moreover, these technologies enable lights-out manufacturing, where factories can operate autonomously, further reducing energy consumption during off-peak hours and lowering operational costs.
4. Digitalized Supply Chains
The adoption of technologies like blockchain and the manufacturing metaverse is improving supply chain resilience and performance. By creating transparent and tamper-proof supply chain networks, blockchain technology enhances traceability and accountability. This not only reduces the risk of counterfeit products but also ensures ethical sourcing and minimizes the environmental impact of the supply chain.
The manufacturing metaverse, on the other hand, facilitates real-time collaboration among stakeholders, optimizing logistics and reducing unnecessary transportation-related emissions.
5. Energy Efficiency
Manufacturers are adopting renewable energy sources and optimizing production flow to reduce their carbon footprint and operational costs. In pursuit of energy efficiency, factories are installing solar panels, wind turbines, and advanced energy management systems to harness clean energy.
Additionally, the implementation of lean manufacturing principles helps minimize energy-intensive processes, resulting in significant reductions in both energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
6. Eco-friendly Packaging Materials and Recycling
A shift towards biodegradable and recycled materials in manufacturing is reducing the need for new raw materials and conserving resources.
Manufacturers are increasingly adopting eco-friendly packaging solutions, such as bioplastics and recyclable materials, to reduce packaging waste. Moreover, recycling initiatives within production facilities ensure that materials are repurposed, reducing the strain on natural resources and promoting a circular economy.
7. Reducing Waste and Water Consumption
Factories are implementing strategies to minimize waste production and water consumption in their operations. Lean manufacturing practices, coupled with waste-to-energy solutions, enable the efficient utilization of resources and the reduction of waste sent to landfills. Water recycling and purification systems further minimize the environmental impact by reducing the overall water footprint of manufacturing processes.
8. Advanced Robotics and Automation
Advanced robotics are being integrated into production lines for precision assembly and enhanced product quality. Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside human operators, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of errors.
These robots are equipped with advanced sensors and vision systems, ensuring safe and efficient collaboration, while also enabling intricate tasks that were once only achievable by skilled human workers.
9. AI for Predictive Maintenance
AI-driven predictive maintenance protocols are maximizing equipment reliability and reducing downtime.
By analyzing data from sensors and IoT devices, AI algorithms predict when machinery is likely to fail and schedule maintenance proactively. This not only extends the lifespan of equipment but also minimizes unscheduled downtime, ensuring uninterrupted production and reducing resource wastage.
10. Supply Chain Resilience
Manufacturers are prioritizing resilient supply chains to navigate uncertainties, diversifying suppliers and optimizing logistics. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of supply chain resilience, prompting manufacturers to reevaluate their sourcing strategies and invest in contingency planning.
By ensuring a steady flow of materials and minimizing disruptions, manufacturers contribute to smoother operations and reduced environmental impact.
![]()
11. Digital Twin Technology
The use of digital twins for creating virtual replicas of physical assets is aiding in optimizing manufacturing designs and processes.
Digital twin technology enables real-time monitoring and simulation of production systems, allowing for predictive adjustments and optimizations. This not only improves product quality but also reduces the need for physical prototypes, minimizing material waste and energy consumption during the design phase.
12. Industrial Automation
Automation technologies are evolving to make manufacturing more accessible and cost-effective, enhancing safety and saving costs. With the advent of low-cost automation solutions, even smaller manufacturers can benefit from streamlined processes and improved safety conditions.
These automation systems can be easily integrated into existing operations, reducing the barrier to entry and promoting sustainability across the industry.
13. Additive Manufacturing
Ongoing innovations in 3D printing are bridging the gap between conventional manufacturing processes and mass production.
Additive manufacturing techniques are becoming more efficient and versatile, allowing for the production of complex, lightweight, and highly customizable parts. This not only reduces material waste but also opens up new possibilities in product design and prototyping.
14. Artificial Intelligence
AI in manufacturing is optimizing production, managing assets, and enabling predictive maintenance. AI algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify patterns and anomalies, improving production efficiency and reducing energy consumption. Additionally, AI-powered asset management systems ensure that machinery operates at peak performance, extending their lifespan and minimizing the need for replacements.
15. Collaborative Assembly Robots
Robotic arms are aiding in repetitive assembly tasks, amplifying the efforts of trained assemblers. These collaborative robots work hand-in-hand with human workers, reducing the physical strain and monotony of repetitive tasks. This not only improves worker satisfaction but also enhances assembly line efficiency and product consistency.
16. Shop Floor Logistics Automation
Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are streamlining industrial workflows with AI- and 3D vision-based technologies. These AMRs navigate factory floors autonomously, transporting materials and components efficiently.
By optimizing logistics and reducing manual material handling, AMRs minimize operational inefficiencies and lower energy consumption in factories.
17. Affordable Metal 3D Printing
Startups are scaling metal 3D printing solutions, making it more accessible for small-to-medium businesses. Metal 3D printing offers the advantages of reduced material waste and the ability to produce complex, lightweight, and customized metal parts.
As the technology becomes more affordable and widespread, its sustainability benefits will be accessible to a broader range of manufacturers.
18. 3D Polymer Printing Technology
High-performance polymers are being used for 3D printing, suitable for aerospace, medical, and electronics industries. This innovation in polymer 3D printing allows for the creation of lightweight and durable components while reducing material waste.
The versatility of polymer printing opens up possibilities for designing eco-friendly products across various sectors.
19. Predictive Maintenance Solutions
AI-based software is enabling predictive maintenance of industrial equipment, leveraging data from IoT sensors. This proactive approach to maintenance not only minimizes unplanned downtime but also optimizes the use of spare parts and resources.
By extending the lifespan of machinery and reducing resource consumption, predictive maintenance contributes to both sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
20. Green Manufacturing Initiatives
Manufacturers are embracing green initiatives to minimize their environmental footprint, focusing on energy-efficient components and waste reduction strategies. From the adoption of green materials to the implementation of circular economy principles, the industry is committed to sustainability.
By aligning business practices with ecological responsibility, manufacturers are driving positive change and shaping a greener future for manufacturing.

Conclusion
The 2024 manufacturing landscape is marked by a significant push towards sustainability and technological innovation. These 20 trends highlight the industry’s commitment to a greener and more efficient future.
As manufacturers continue to adapt and embrace these changes, they not only meet the current demands but also pave the way for a sustainable and innovative future in manufacturing.
References:
- https://incit.org/en/thought-leadership/whats-in-store-for-2024-5-top-manufacturing-trends-to-watch/
- https://www.mau.com/blog/workforce-insights/the-future-of-sustainable-manufacturing-top-trends-and-innovations/
- https://www.miscontrols.com/5-trends-2024/
- https://www.startus-insights.com/innovators-guide/manufacturing-trends-innovation/